17 Main Types of Solar Inverters
 Jul 19,2022
Jul 19,2022

 Rekesun
Rekesun
Depending on the input source, connection method, output voltage waveform, etc. of the application, solar inverters are divided into the following 17 main categories.
1. Classification by input source
Voltage Source Solar Inverter
When the input of a solar inverter is a constant DC voltage source, the solar inverter is called a voltage source solar inverter. The input of the voltage source solar inverter has a rigid DC voltage source with zero impedance. In practice, the impedance of the DC voltage source is negligible.
Current Source Solar Inverter
When the input of a solar inverter is a constant DC current source, the solar inverter is called a current source solar inverter. Rigid current is supplied to the CSI from a DC power source, which has a high impedance.
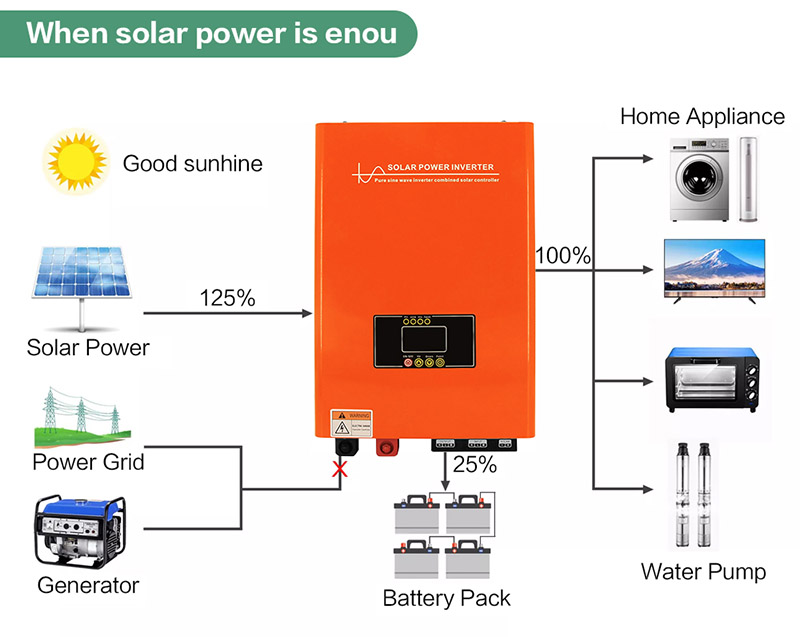
2. Classification by output phase
Single Phase Solar Inverter
A single-phase solar inverter converts a DC input to a single-phase output. The output voltage/current of a single-phase solar inverter is only one phase with a nominal frequency of 50Hz or a nominal voltage of 60Hz.
Three Phase Solar Inverter
Three-phase solar inverters convert direct current to three-phase power. The three-phase power supply provides three-way alternating current that is evenly separated. All three waves produced at the output have the same amplitude and frequency but vary slightly due to the load, while each wave is 120 degrees out of phase with respect to each other.
3. Classification by commutation technology
line commutation
In these types of solar inverters, the line voltage of the AC circuit is available through the device, which is turned off when the current in the SCR experiences a zero characteristic. This commutation process is called line commutation, and a solar inverter that works on this principle is called a line commutated solar inverter.
forced commutation
In this type of commutation, there is no zero point in the power supply. This is why some external resources are required to rectify the device. This commutation process is called forced commutation, and solar inverters based on this process are called forced commutation solar inverters.
4. Classification by connection method
Series Solar Inverter
A series solar inverter consists of a pair of thyristors and an RLC (resistive, inductive and capacitive) circuit. One thyristor is connected in parallel with the RLC circuit, and one thyristor is connected in series between the DC power supply and the RLC circuit. Such solar inverters are called series solar inverters because the load is directly connected in series with the DC source with the help of thyristors.
Parallel solar inverters
A parallel solar inverter consists of two thyristors, a capacitor, a center-tapped transformer, and an inductor. A thyristor is used to provide a path for the current to flow, while an inductor is used to keep the current source constant. Turning on and off of these thyristors is controlled by commutation capacitors connected between them. It is called a shunt solar inverter because in operation, the capacitor is connected in parallel with the load through the transformer.
Half-Bridge Solar Inverter
Half-bridge solar inverters require two electronic switches to work. Switches can be MOSFETs, IJBTs, BJTs or thyristors. Half bridges with thyristors and BJT switches require two additional diodes, except for purely resistive loads, while MOSFETs have built-in body diodes.
Full Bridge Solar Inverter
A single-phase full-bridge solar inverter has four controlled switches that control the direction of current flow in the load. The bridge has 4 feedback diodes that feed back the energy stored in the load back to the source.
Three Phase Bridge Solar Inverter
Industrial and other heavy loads require three-phase power. To run these heavy loads from storage devices or other DC sources, a three-phase solar inverter is required.
5. according to the operation mode classification
Off Grid Solar Inverter
Off-grid solar inverters can power the load on their own without being affected by the grid or other power sources.
Grid-tied solar inverter
A grid-tied solar inverter has two main functions. One function of a grid-tied solar inverter is to provide AC power from a storage device to an AC load, while another function of a grid-tied solar inverter is to provide additional power to the grid.
Bimodal solar inverter
Bimodal solar inverters can work both as grid-tied solar inverters and off-grid solar inverters.
6. Classification by output waveform
Square wave solar inverter
These are the simplest solar inverters that convert DC to AC, but the output waveform is not the desired pure sine wave, these solar inverters have square waves at the output.
Quasi-sine wave solar inverter
Quasi-sine wave solar inverter or simply modified sine wave solar inverter with stepped sine wave.
Pure Sine Wave Solar Inverter
Pure sine solar inverters convert DC to almost pure sinusoidal AC, the output waveform of pure sine wave solar inverters is still not an ideal sine wave, but much smoother than square wave and quasi-sine wave solar inverters.
7. Classification according to the number of output levels
Two Level Solar Inverter
Two-level solar inverters have two output levels, where the output voltage alternates between positive and negative, and has a fundamental frequency.
Multilevel Solar Inverter
The multi-level solar inverter converts the DC signal into a multi-level ladder waveform. The output waveform of the multi-level solar inverter is not directly alternating positive and negative, but multi-level alternating.


 Home
Home Selection skills of photovoltaic high-frequency inverters
Selection skills of photovoltaic high-frequency inverters 







 syplighting.en.alibaba.com
syplighting.en.alibaba.com



